MDF & Co-Op Funds
Invest in partner success with transparent, easy-to-use market development funds. Simplify requests, prove ROI, and ensure your MDF program drives real results instead of becoming a frustration point.
MDF programs that partners actually use
Low MDF utilization isn't a partner problem—it's a process problem. When approval workflows are unclear, reimbursement takes months, or requirements are buried in documents, partners abandon the program. Unifyr provides transparent processes, automated workflows, and real-time tracking that encourage utilization. More partners using funds means more joint marketing, more pipeline, and better ROI on your channel investment.

Simple request process
Partners submit MDF requests through the portal with clear guidelines on eligible activities and required documentation. No confusion, no endless email chains—just straightforward processes that encourage use.
Automated approval workflows
Route requests based on amount, activity type, or partner tier. Set auto-approval thresholds for qualified partners and pre-approved activities to eliminate delays on routine requests.
Complete audit trails
Track every request from submission to reimbursement with full documentation and approval history. Maintain compliance and answer finance questions instantly with transparent records.
Track MDF performance, not just MDF spend
MDF programs fail when you can't connect spend to results. Unifyr ties MDF requests to campaign performance, lead generation, and pipeline impact. See which activities drive ROI, which partners use funds effectively, and where to adjust your program. Prove to finance that MDF is an investment, not an expense.
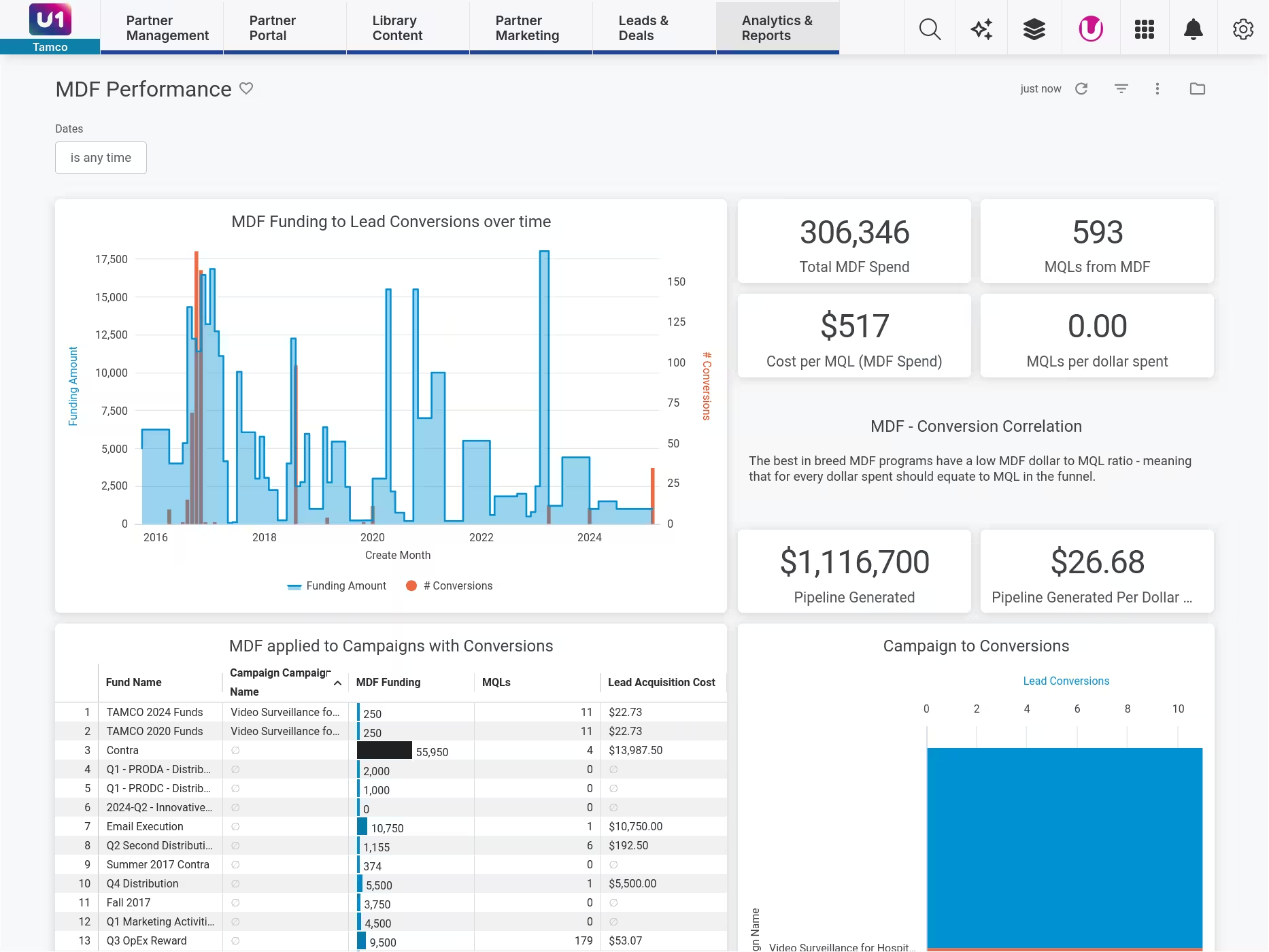
Complete visibility into fund utilization
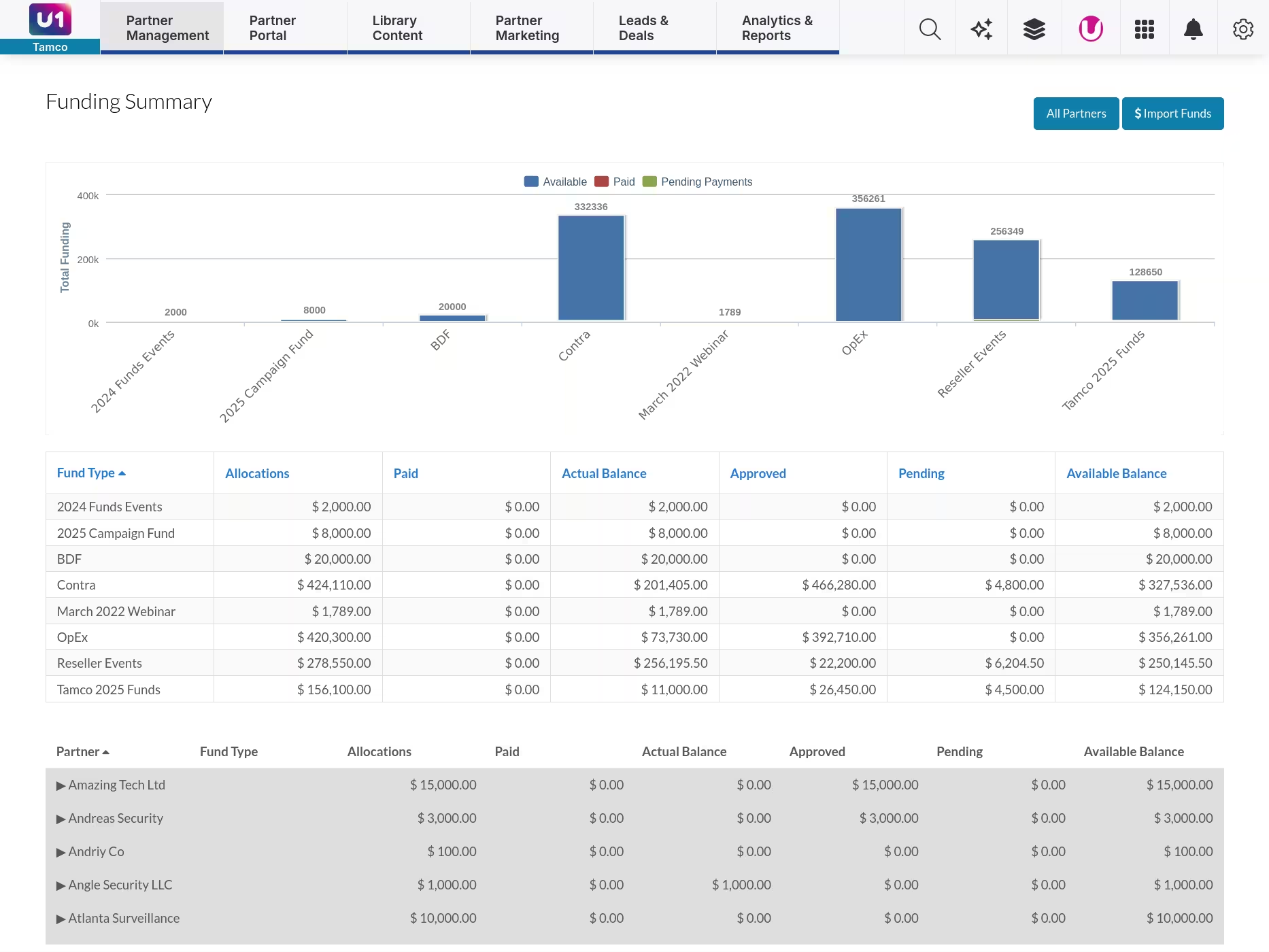
Track allocation, usage, and remaining balance across your entire partner ecosystem. See which partners actively use funds, where budget sits idle, and which activities drive results. Unifyr's funding dashboard provides real-time visibility into spend patterns, helping you optimize budget allocation and prove program impact to finance.
 Feature
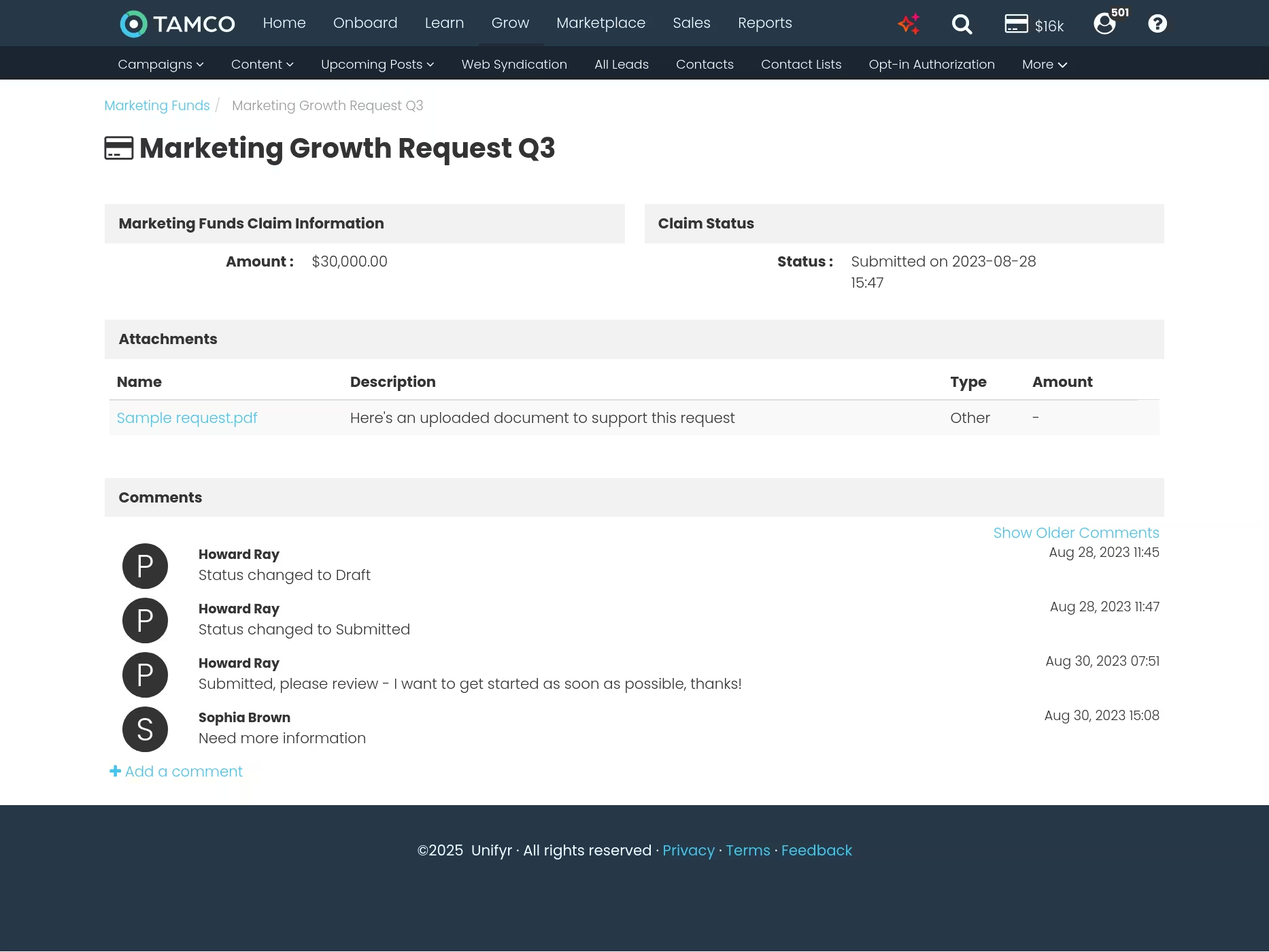
FeatureStreamlined request and approval
Partners submit MDF requests with clear forms that capture all required information—campaign details, budget breakdown, expected outcomes, and supporting documentation. Automated workflows route requests based on amount, activity type, or partner tier. Set auto-approval for pre-qualified activities to eliminate delays. Partners receive instant notifications on approvals, rejections, or requests for more information, keeping everyone aligned without constant follow-up.
 Feature
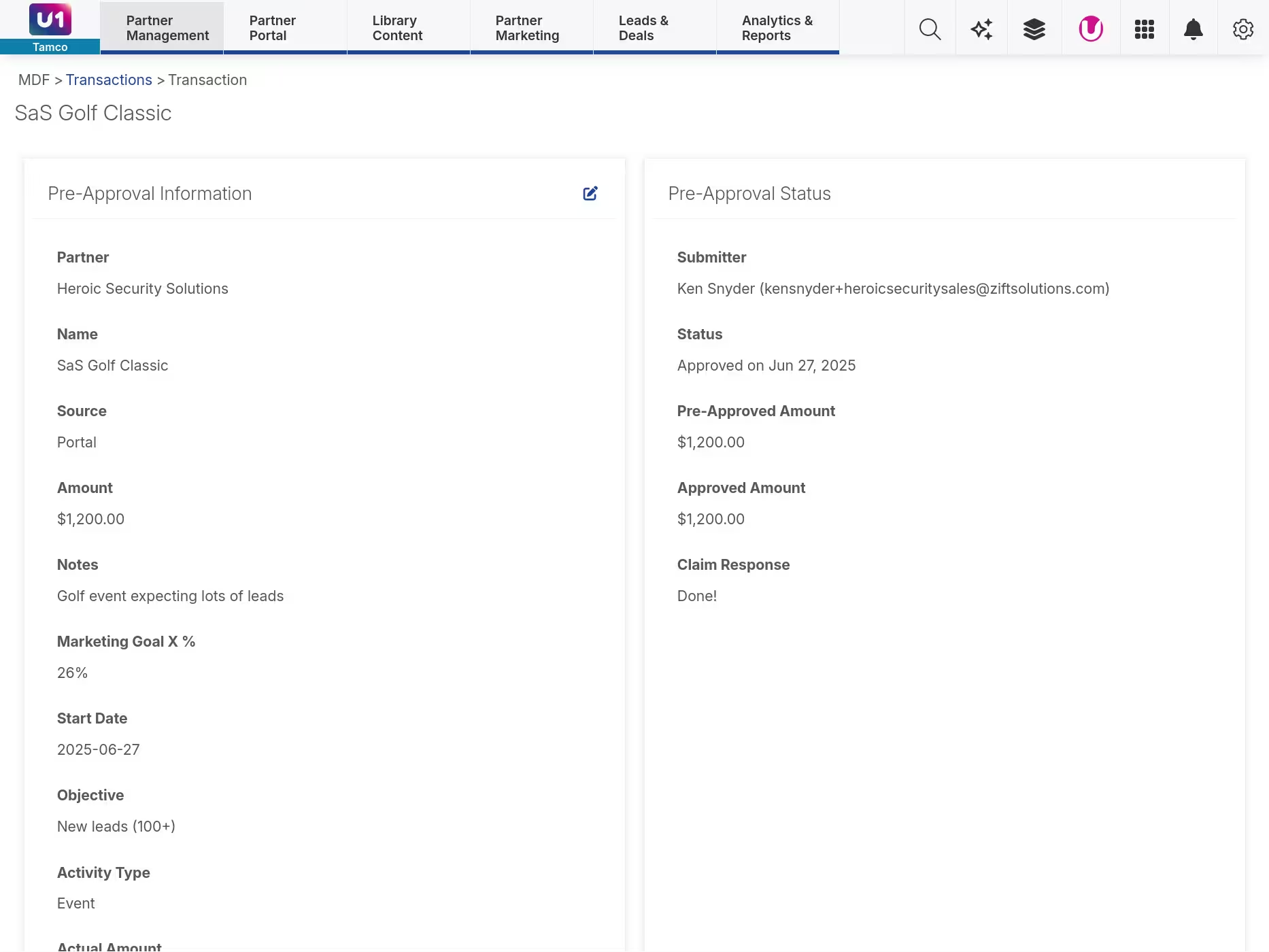
FeatureComplete transaction history
Track every MDF transaction from allocation to reimbursement with full audit trails. See request details, approval decisions, proof-of-performance documentation, and payment status in one view. Finance teams get the documentation they need for compliance, channel managers answer questions instantly, and partners understand exactly where their funds went. No spreadsheets, no email archaeology—just transparent records everyone can trust.
Market Development Funds (MDF) are vendor-provided resources that partners use for approved marketing and sales activities—campaigns, events, training, or demand generation. Co-op funds typically refer to reimbursement programs based on past sales performance, while MDF focuses on future opportunity creation.
The distinction matters less than the execution. Both programs exist to invest in partner success and drive joint revenue. The challenge is making these programs easy to use, trackable, and demonstrably effective. Partners want clarity on what's eligible, fast approvals, and timely reimbursement. Vendors need attribution data showing that funds drive pipeline and revenue.
ROI measurement starts with connecting MDF activities to outcomes. When a partner uses funds for a campaign, track the leads generated, opportunities created, and revenue influenced. Unifyr ties MDF requests to campaign performance automatically, so you can report on cost-per-lead, pipeline-to-spend ratios, and ultimately revenue return.
The key is setting expectations upfront. Different activities have different timelines—demand generation may show results in weeks, while partner readiness investments (training, certifications) take months. Define what success looks like for each activity type, track it consistently, and review results in partner business reviews. This data becomes your case for continued or increased MDF funding.
Yes. Unifyr lets you define eligible activities, set approval rules by partner tier, and create different MDF programs for different partner types. You might offer demand generation funds to top-tier partners while focusing newer partners on readiness activities like training and certification. Or restrict certain high-investment activities (like major events) to partners who meet performance thresholds.
Segmentation ensures your MDF budget goes where it drives the most impact. Partners at different maturity stages need different support. Clear guidelines prevent frustration and misaligned expectations on both sides.
Unifyr replaces email chains and spreadsheets with a portal-based system where partners submit requests with all required details and documentation upfront. Automated workflows route requests to the right approvers based on your rules. Partners see real-time status updates instead of waiting days for responses.
For pre-approved activities or qualified partners, you can set auto-approval rules that eliminate manual review entirely. This speeds time-to-market for partners and reduces administrative load for your team. All activity is logged with full audit trails for compliance and finance reporting.
Unifyr provides dashboards showing total MDF spend, utilization rates by partner, request approval times, activity breakdown, and campaign performance tied to funded activities. See which partners use funds effectively, which activity types drive best results, and where budget is underutilized.
These insights help you optimize your program over time—shift budget toward high-performing activities, identify partners who need more support or guidance, and prove program value to executives with clear attribution data. Reports are exportable for finance integration and board presentations.